Modulo Multiplication Rules
72 The exponent next to the 10 is not necessary but we place it there to make the next step slightly easier. Multiplication rule In this video I prove to you the multiplication rule for two complex numbers when given in modulus-argument form.

Multiplication And Division Rules For Mod And Argument Of Two Complex Numbers Examsolutions
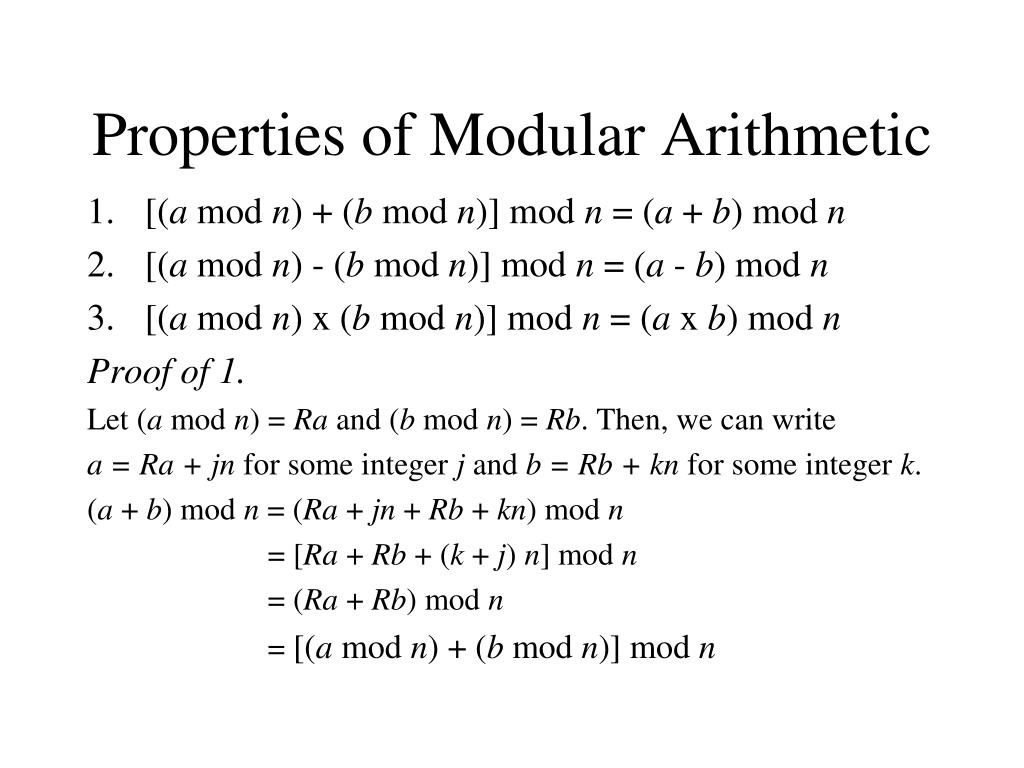
A b mod m a mod m b mod m mod m.
Modulo multiplication rules. 15 17 7 15 7 17 7 7 1 3 7 4 7 4 Same rule is for modular subtraction. 5 equiv 2 bmod 3 8 equiv 2 bmod 3. This is the currently selected item.
Rule for modular addition is. Okay thats how addition works in modular arithmetic. B mod C R2.
Modular Addition. A C Q1 R1 where 0 R1 C and Q1 is some integer. Clearly this set of numbers is closed under multiplication has associative multiplication and contains 1 so it remains to show that these are precisely the invertible elements.
By Lemma 1 we can do this i a and n are coprime. 101 1 mod 3. This says that if we multiply integer times integer and take the product modulo we get the same answer as if we had first taken modulo and multiplied by modulo and taken that product modulo.
We will prove that A B mod C A mod C B mod C mod C. 2x1x2y1y2 x1 2 y2 2 y1 2 x2 2 and we get 0 y1x2-x1y2 2. Multiply both sides by -12.
Proof for Modular Multiplication. Rule for modular multiplication is. Addition and multiplication are well-defined modulo m.
September 22 2019 Craig Barton Modulo arithmetic Number. In modular arithmetic there are two equivalent expressions. Division rule In this video I prove to you the division rule for two complex numbers when given in modulus-argument form.
Modular multiplication is pretty straightforward. There are two ways we can go about doing this. Say that at this point we want to determine the remainder of 100 after dividing it by 3.
In computing the modulo operation returns the remainder or signed remainder of a division after one number is divided by another called the modulus of the operation. Applying the rules of indices to form and solve equations. The central definition in studying modular arithmetic systems establishes a relationship between pairs of numbers with respect to a special number m called the modulus.
1 is the unit element. B C Q2 R2 where 0 R2 C and Q2 is some integer. The language of modular arithmetic we can write.
Square both sides again. Dont forget this other important rule. This is equivalent to solving axny 1 in integers.
For example say the modulus is 7. Given two positive numbers a and n a modulo n abbreviated as a mod n is the remainder of the Euclidean division of a by n where a is the dividend and n is the divisorThe modulo operation is to be distinguished from the. One thing to notice is that in modular arithmetic you can multiply two numbers that are both.
The rule for doing multiplication in modular arithmetic is. The order of an element n i of this group is denoted by ord mn i. That is If aequiv bbmod m and cequiv dbmod m then acequiv bdbmod m and acequiv bdbmod m.
Two integers a and b are congruent modulo m if they dier by an integer multiple of m ie b a km for some k 2 Z. Suppose we want to solve ax 1modntoinverta. 517 or the theory of.
This equivalence is written a b mod m. It works just like modular addition. From the quotient remainder theorem we can write A and B as.
Modular multiplication appears in many fields of mathematics and has many far-ranging applications including cryptography computer science and computer algebra. Of multiplication modulo mwith the product rule 2 n i mod mn j mod m n in j mod m. When the result is a negative number add multiples of the modulus until you end up with a number between 0 and the modulus minus 1.
If a b c a cdot b c a b c then a m o d N b m o d N c m o d N apmod Ncdot bpmod N equiv c pmodN a m o d N b m o d N c m o d N. For example in arithmetic modulo 12 like what we have when adding numbers on a normal 12-hour clock a problem like 10 5 mod 12 has the answer 3 and not 15 since once we count up to 12 we start over at 1 again. Ab equiv a_1b_1 equiv c_1 bmod n For example.
Properties of multiplication in modular arithmetic. We dont require much modular subtraction but it can also be done in same way. Multiplying and dividing algebraic fractions.
From Eulers theorem of number theory 1 Thm. You just multiply the two numbers and then calculate the standard name. Modulo Challenge Addition and Subtraction Modular multiplication.
A mod C R1. Lets look at some mod 15 examples. Below are some interesting properties of Modular Multiplication a x b mod m a mod m x b mod m mod m.
A bmod n a_1 iff a equiv a_1 bmod n b bmod n b_1 iff b equiv b_1 bmod n ab bmod n c_1 iff ab equiv c_1 bmod n According to the multiplication property see. We must show that LHS RHS.

Modular Arithmetic Rules Properties Video Lesson Transcript Study Com

Ppt Modular Arithmetic Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4352697

How To Prove This Modular Multiplication Property To Be True Mathematics Stack Exchange

Modular Arithmetic This Lecture Modular Arithmetic Is An
Posting Komentar untuk "Modulo Multiplication Rules"